Subject–verb agreement is one of the most important grammar rules in the English language. It ensures that a sentence is grammatically correct, clear, and easy to understand. Whether in speaking or writing, correct subject–verb agreement improves fluency, accuracy, and professionalism.
In simple terms, subject–verb agreement means that the verb must agree with the subject in number and person. A singular subject takes a singular verb, and a plural subject takes a plural verb.
What Is Subject–Verb Agreement?
Subject–verb agreement refers to the grammatical rule that the verb in a sentence must match the subject. If the subject is singular, the verb should be singular. If the subject is plural, the verb should be plural.
Examples:
- She works hard.
- They work hard.
Here, she is singular, so the verb takes -s, while they is plural, so the base form of the verb is used.
Why Is Subject–Verb Agreement Important?
Correct subject–verb agreement:
- Improves sentence clarity
- Enhances writing accuracy
- Prevents grammatical errors
- Builds professional communication skills
- Increases confidence in spoken English
Incorrect agreement can confuse readers and reduce the credibility of the speaker or writer.
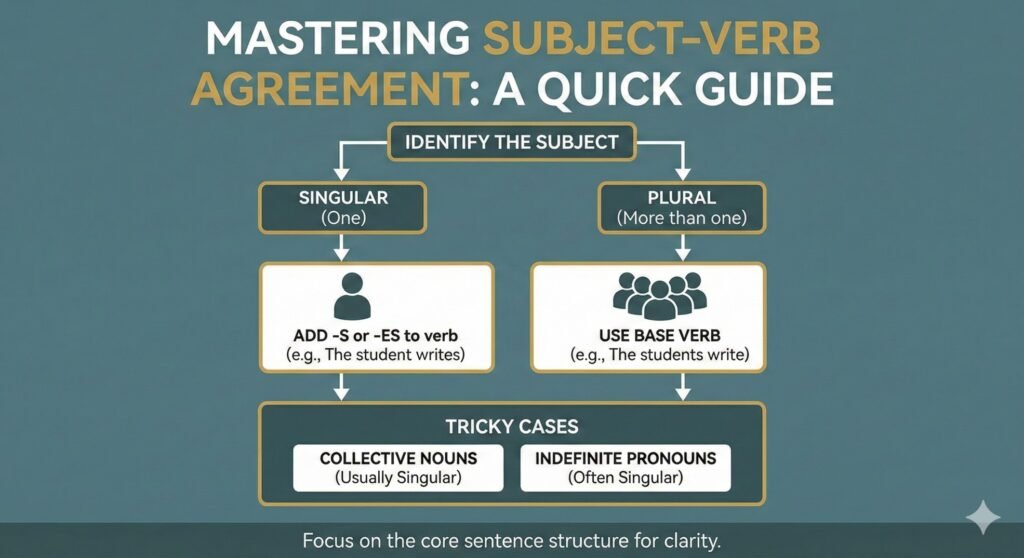
Basic Rules of Subject–Verb Agreement
1. Singular Subject → Singular Verb
A singular subject takes a singular verb, usually ending in -s or -es in the present tense.
Examples:
- The boy plays football.
- She teaches English.
2. Plural Subject → Plural Verb
A plural subject takes a plural verb (base form without -s).
Examples:
- The boys play football.
- They teach English.
3. Compound Subjects Joined by “and” → Plural Verb
When two subjects are joined by and, the verb is plural.
Examples:
- Ali and Ahmed are classmates.
- The teacher and the students are in the classroom.
4. Subjects Joined by “or” / “nor” → Verb Agrees with Nearest Subject
When subjects are connected by or or nor, the verb agrees with the nearest subject.
Examples:
- Either the teacher or the students are responsible.
- Either the students or the teacher is responsible.
5. Collective Nouns
Collective nouns (team, group, family, committee) can be singular or plural depending on meaning.
- Singular when acting as one unit:
- The team is winning.
- Plural when individuals act separately:
- The team are arguing among themselves.
6. Indefinite Pronouns
Some pronouns are always singular, some always plural, and some depend on context.
Always Singular:
everyone, someone, nobody, each, everybody
- Everyone is ready.
Always Plural:
few, many, several
- Many are absent today.
7. Uncountable Nouns → Singular Verb
Uncountable nouns such as water, information, advice, furniture take singular verbs.
Examples:
- The information is correct.
- The furniture is expensive.
8. Titles, Distances, Amounts, and Time → Singular Verb
Even if plural in form, these take a singular verb.
Examples:
- Ten kilometers is a long distance.
- Five years is a long time.
Common Errors in Subject–Verb Agreement
❌ The list of items are on the table.
✅ The list of items is on the table.
❌ Everyone know the answer.
✅ Everyone knows the answer.
❌ Neither of the students are late.
✅ Neither of the students is late.
Tips to Master Subject–Verb Agreement
- Identify the main subject of the sentence.
- Ignore phrases between the subject and verb.
- Watch out for tricky structures with or, nor, each, everyone, none.
- Practice regularly with exercises and real-life sentences.
Importance of Subject–Verb Agreement in Professional Communication
Correct grammar reflects professionalism. In emails, reports, presentations, and academic writing, accurate subject–verb agreement builds credibility, clarity, and confidence.
For students, job seekers, professionals, and safety officers, proper grammar strengthens communication and career growth.
Conclusion
Subject–verb agreement is a fundamental rule of English grammar that ensures clarity and correctness in communication. By mastering its rules and practicing regularly, learners can significantly improve their spoken and written English.
Strong grammar leads to stronger communication—and stronger communication leads to greater success.
